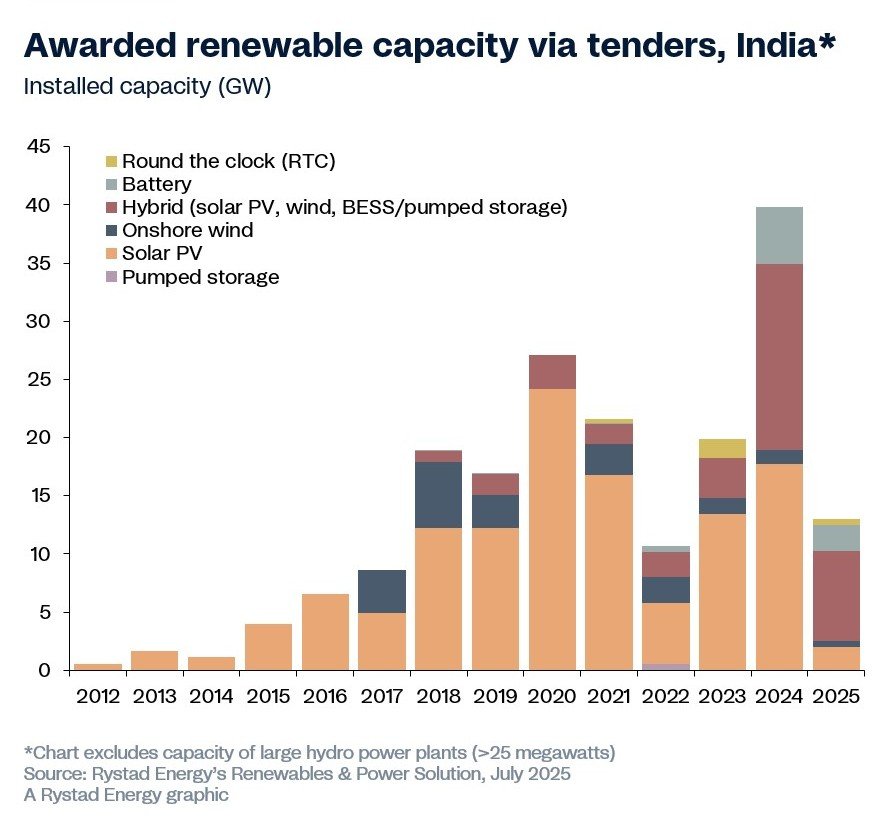
India’s 7.6 GW Battery Storage Leap in 2025 Signals Renewable Energy Transformation
India has made a significant breakthrough in renewable energy adoption by awarding 7.6 gigawatts (GW) of battery energy storage systems (BESS) in the first half of 2025, according to Rystad Energy. This allocation represents the nation’s largest energy storage commitment to date, comprising 5.4 GW of colocated hybrid solar systems and 2.2 GW of standalone BESS projects.
Why India’s Battery Storage Expansion Matters
Solar panels alone cannot address India’s increasing energy demands. Battery storage plays a crucial role in grid stability by storing excess solar energy during peak production and releasing it during high demand periods. This development supports India’s clean energy transition while reducing dependence on coal-fired power plants.
Key Statistics and Market Trends
- Average tariffs: INR 4,000 ($48.02)/MWh for standalone BESS vs. INR 3,208 ($38.50)/MWh for solar-BESS hybrids
- Major developers like NTPC and Jindal Group secured nearly 1 GW each in colocated capacity
- Significant cost reductions compared to previous years’ storage projects
Economic Viability of Battery Storage
While battery storage requires substantial upfront investment, long-term benefits include reduced transmission costs and peak-time energy sales. The economics mirror residential solar solutions where initial costs are offset by years of reliable, low-cost energy.
Future Implications for India’s Energy Sector
This storage expansion may accelerate grid parity where renewables compete directly with fossil fuels. The growth aligns with the India energy stack revolution as the nation modernizes its power infrastructure to accommodate increasing renewable capacity.
Experts predict developers will increasingly favor hybrid models over standalone solar farms, particularly as storage costs continue their downward trajectory.